NERDIO GUIDE

Beyond a conference — NerdioCon 2026: Learning, networking & unforgettable moments.
Save your spot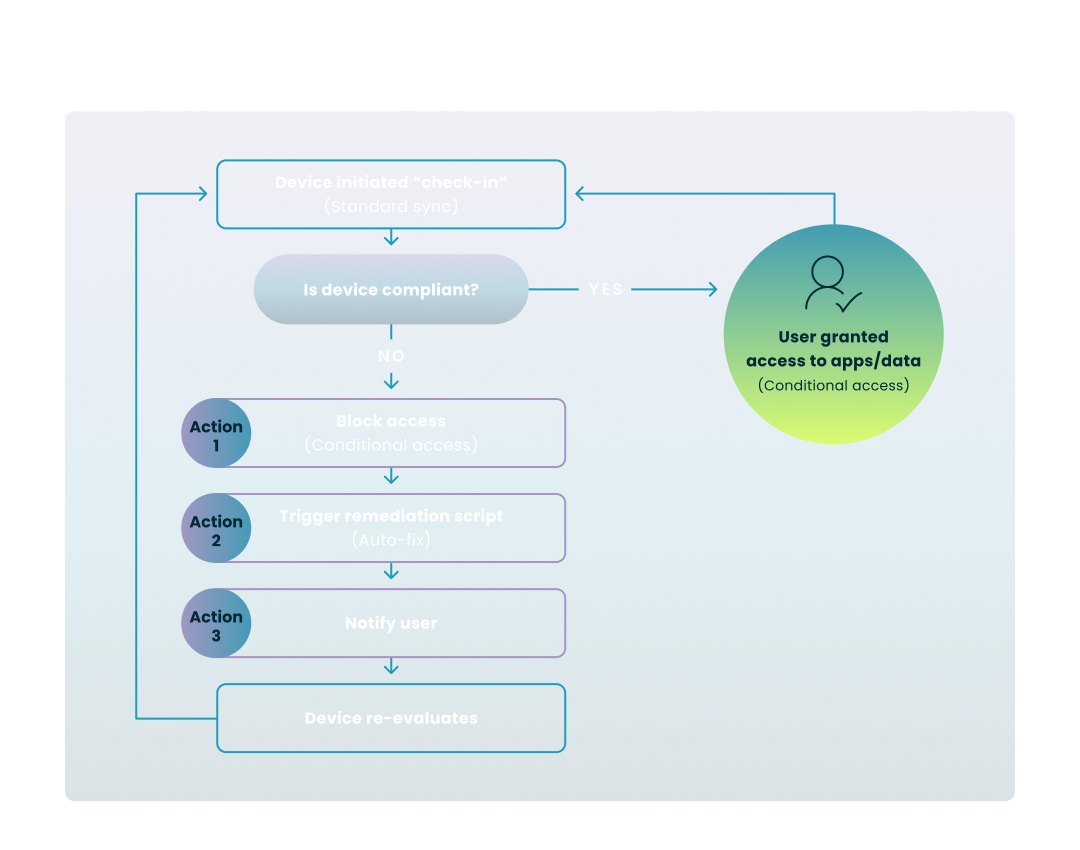
NERDIO GUIDE
Carisa Stringer | December 22, 2025
Managing endpoint security at an enterprise scale requires more than just setting rules; it demands intelligent automation. Automating compliance and security policies in Intune transforms static configurations into a dynamic defense system, ensuring devices remain secure without constant manual intervention.
By leveraging native features like Conditional Access and automated remediation scripts, IT teams can enforce zero-trust principles across physical laptops, Azure Virtual Desktop session hosts, and Windows 365 Cloud PCs simultaneously. However, as environments grow, bridging the gap between native capabilities and enterprise needs—such as third-party patching and policy rollback—becomes the critical challenge for modern IT leadership.
Automated compliance is the process of continuously monitoring and enforcing security standards across your entire device estate without manual IT involvement. As a comprehensive cloud-based endpoint management solution, Microsoft Intune enables IT teams to secure and manage all their user devices and applications from a single unified console, serving as the critical engine for these automated compliance checks.
Rather than checking devices individually, you define a "desired state" (e.g., BitLocker enabled, minimum OS version), and Intune automatically measures every device against this standard during its check-in cycle. This architecture relies on modern mobile device management standards to push configurations over the internet, ensuring that security policies are applied consistently regardless of whether the device is in the office or remote.
To better understand how these active protections function in real-time, the following diagram illustrates the continuous cycle of evaluation and enforcement that occurs on every managed device.
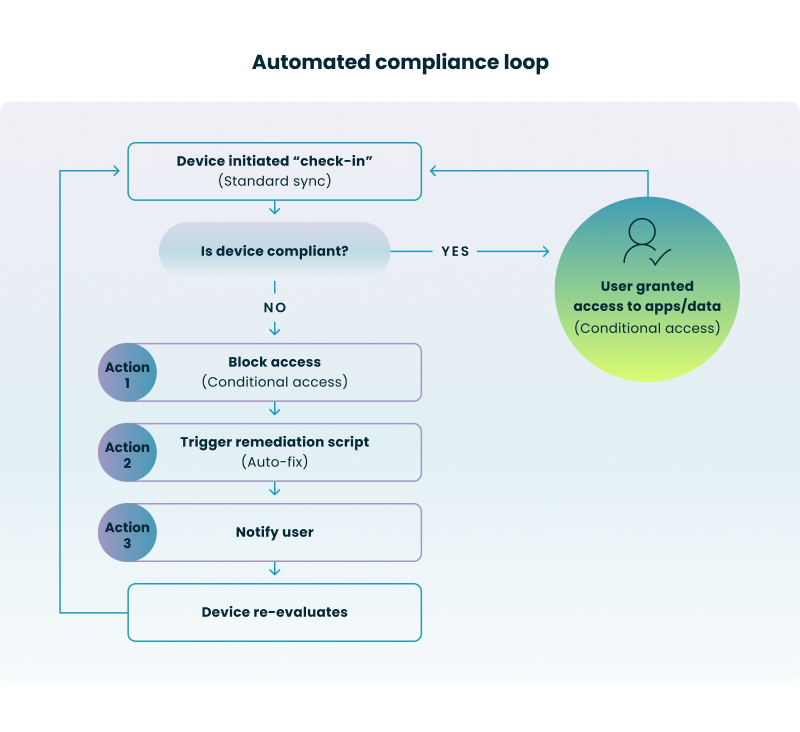
How the Cycle Works:
The most effective security is preventative. By automating the application of security baselines, you ensure that every new device—whether a physical laptop or a cloud PC—is "born secure" the moment it is provisioned.
When a device fails a compliance check, you cannot afford to wait for a help desk ticket. You need an automated response that protects your environment immediately.
While the native features described above are powerful, they often hit a ceiling in large, complex enterprise environments. "Textbook" Intune management can struggle with the messy reality of hybrid infrastructure and diverse application landscapes.
To overcome these enterprise-scale hurdles, many organizations turn to unified management platforms like Nerdio Manager for Enterprise. These platforms act as an enterprise-grade automation layer that sits securely on top of your Microsoft tenant.
To visualize this architecture, the diagram below illustrates how a unified platform operates as a cohesive automation layer above your existing Microsoft infrastructure, rather than replacing it.
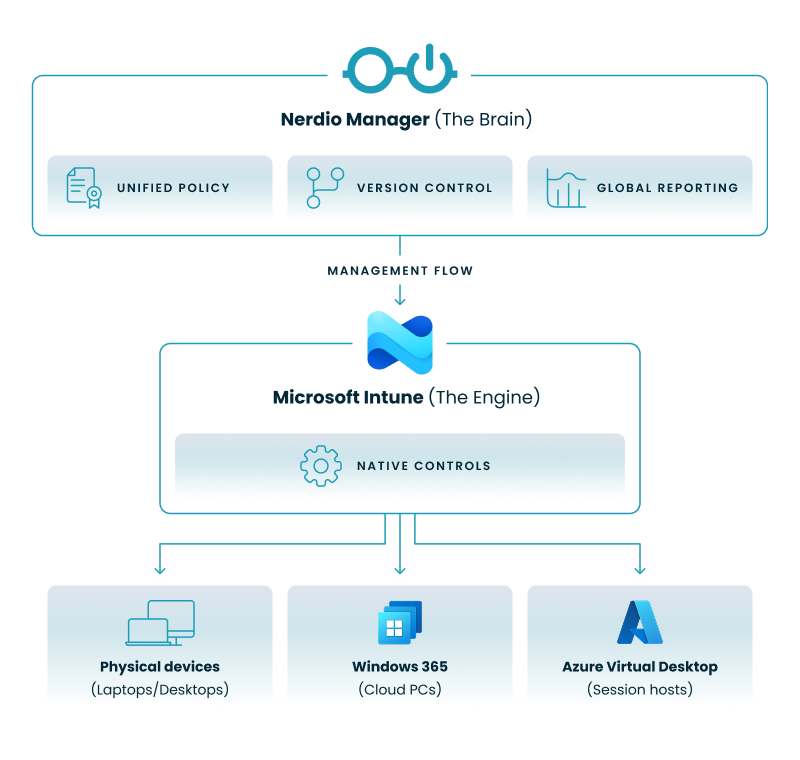
To move from basic management to true automated security, you need to evaluate your current maturity level and identify where your gaps lie.
Nerdio Manager can automate your third-party patching and provide instant policy rollback for your Intune environment. See how.
See how you can optimize processes, improve security, increase reliability, and save up to 70% on Microsoft Azure costs.
To configure device compliance policies in Intune, you must sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center, navigate to Devices > Compliance, and select Create policy. From there, you specify the platform (such as Windows 10 or iOS), configure the specific security settings—such as requiring BitLocker or a minimum OS version—and assign the policy to the relevant user or device groups.
The difference between Intune and Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM) is that Microsoft Intune is the cloud-based MDM/MAM service for managing mobile and cloud-first endpoints. For hybrid management combining cloud and on-premises infrastructure, Intune can co-exist with Microsoft Configuration Manager (formerly SCCM). Together, these tools provide unified endpoint management capabilities. While Intune focuses on cloud-first management, Endpoint Manager provides a unified interface to manage both cloud and on-premises endpoints through a single console.
The default device compliance behavior in Intune is controlled by the "Mark devices with no compliance policy assigned as" setting, which determines whether devices without a specific policy are treated as Compliant or Not compliant. By default, this is often set to "Compliant" for new tenants, but security best practices recommend changing this to "Not compliant" to ensure that no device accesses resources without first passing a security check.
Intune differs from traditional solutions like Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM/SCCM) by being a completely cloud-based service designed for internet-connected devices, whereas MECM relies on on-premises servers and is better suited for granular control of complex, internal networks. While MECM uses an agent-based approach for deep server and desktop management, Intune leverages modern mobile device management APIs to manage endpoints regardless of their physical location.
Microsoft Intune supports a wide range of global compliance certifications and standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type 2, HIPAA, and FedRAMP High, ensuring it meets strict regulatory requirements for various industries. Additionally, Intune provides built-in security baselines that align with frameworks like NIST and CIS to help organizations maintain a secure posture. However, native Intune baselines are not formally CIS or NIST certified. If your organization requires certified CIS Level 1 or Level 2 compliance, consider third-party solutions like Nerdio Manager which offer CIS-certified baseline templates that achieve certified compliance.
You can automate security policy enforcement using Intune by integrating Compliance Policies with Conditional Access, which automatically blocks access to corporate data if a device fails to meet security requirements. For comprehensive automation, unified platforms like Nerdio can extend these capabilities by automatically enrolling Windows 365 and Azure Virtual Desktop environments into Intune and applying remediation scripts to fix vulnerabilities without manual intervention.




Carisa Stringer
Head of Product Marketing
Carisa Stringer is the Head of Product Marketing at Nerdio, where she leads the strategy and execution of go-to-market plans for the company’s enterprise and managed service provider solutions. She joined Nerdio in 2025, bringing 20+ years of experience in end user computing, desktops-as-a-service, and Microsoft technologies. Prior to her current role, Carisa held key product marketing positions at Citrix and Anthology, where she contributed to innovative go-to-market initiatives. Her career reflects a strong track record in driving growth and adoption in the enterprise technology sector. Carisa holds a Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology.