Windows Autopatch
This guide provides an objective overview of Windows Autopatch, covering how it works, benefits for enterprises, prerequisites, comparisons, and expert insights.

This guide provides an objective overview of Windows Autopatch, covering how it works, benefits for enterprises, prerequisites, comparisons, and expert insights.
Carisa Stinger | May 19, 2025
Windows Autopatch is a cloud-based service from Microsoft that automates the process of keeping Windows and Microsoft 365 apps up to date on enrolled devices. It’s included with certain Microsoft 365 subscriptions—like Enterprise E3 and E5—and is designed to reduce the operational overhead of managing updates. Autopatch handles patch deployment for Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams.
By using deployment rings and monitoring update health, it helps ensure that updates are rolled out safely and consistently across your organization. This allows your IT team to maintain security and productivity without manual intervention or complex scheduling.
Windows Autopatch automates the update process for Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, Edge, and Teams, aiming to enhance security and minimize disruptions. It utilizes deployment rings and monitoring to ensure updates are rolled out safely and consistently across your organization.
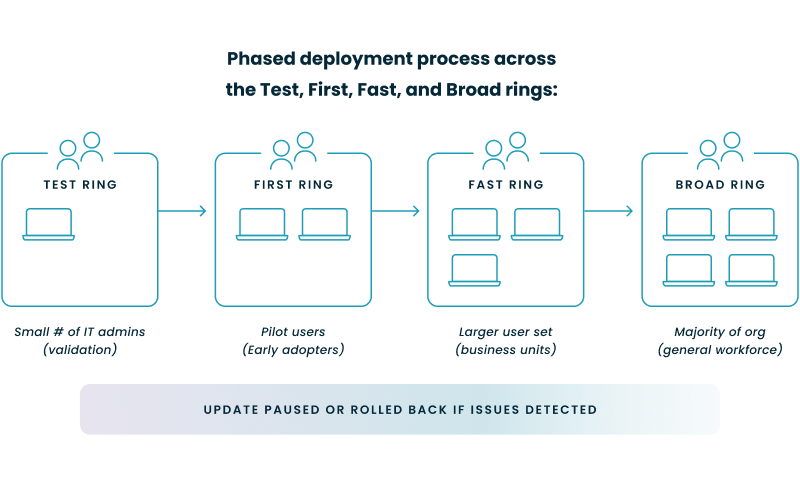
Windows Autopatch manages the deployment of updates for Windows 10/11, Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams. It uses a phased rollout approach with deployment rings—Test, First, Fast, and Broad—to gradually release updates, allowing for monitoring and issue detection at each stage. This process helps ensure that updates are applied smoothly and reduces the risk of widespread issues.
Windows Autopatch offers several features to streamline update management:
By deploying updates in phases and monitoring their impact, Windows Autopatch aims to minimize disruptions to end users. If issues are detected in earlier deployment rings, the rollout can be paused or adjusted before reaching a broader audience. This approach helps maintain productivity and reduces the likelihood of widespread problems.
Windows Autopatch enhances your organization's security posture and compliance by ensuring devices are consistently updated and monitored. Through automated update deployment and comprehensive reporting, it helps maintain system integrity and meet regulatory standards.
By automating the deployment of updates for Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, Edge, and Teams, Windows Autopatch ensures that devices receive the latest security patches promptly. This is especially critical for operating systems like Windows 11 Enterprise, which provides a foundation of advanced, built-in security features; Autopatch's automated updates ensure these defenses are continuously reinforced against emerging threats. This reduces exposure to known vulnerabilities and helps maintain a secure environment.
Windows Autopatch provides detailed reporting through Microsoft Intune, offering insights into update compliance and device health. These reports help you monitor the status of updates across your organization and address any issues proactively.
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for Windows 365 in your organization.
Windows Autopatch streamlines update management, allowing your IT team to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance. By automating update deployment and monitoring, it reduces manual workloads and enhances operational efficiency.

This streamlined approach also proves highly effective for managing Cloud PCs; these virtual desktops, which host a user's personalized Windows environment in the cloud, benefit from Autopatch ensuring they remain consistently updated, thereby enhancing security and user productivity with minimal IT intervention.
Furthermore, Autopatch is particularly valuable in Desktop as a Service (DaaS) scenarios, where businesses leverage cloud-hosted virtual desktops for flexibility and simplified IT management; Autopatch ensures these DaaS environments are consistently patched, maintaining security and performance without requiring extensive manual oversight from the IT team. Similarly, for organizations that have implemented Azure VDI solutions, Autopatch provides an essential layer of automated update management, ensuring that these virtual Windows environments remain current and protected with minimal IT effort.
Maintaining the Windows instances within a complex VDI infrastructure, which encompasses the servers, storage, and networking components necessary to host virtual desktops, is simplified by Windows Autopatch, as it automates updates to the guest operating systems, thereby enhancing security and reducing the patching burden on IT teams responsible for the underlying platform.
Autopatch integrates with Microsoft Intune, a cloud-based service providing comprehensive endpoint management that allows IT to control device configurations and application deployments; this foundational platform is then utilized by Autopatch for managing update rings, monitoring compliance, and reporting on overall device health. Through Intune, you can monitor update compliance, device health, and manage Autopatch groups and deployment rings. This integration simplifies the update management process and enhances visibility across your device fleet.
To utilize Autopatch effectively, your organization must meet specific licensing and technical prerequisites. These requirements ensure that your devices are compatible with the service and can be managed seamlessly through Microsoft Intune. For organizations utilizing Windows 365, which delivers a full, personalized Cloud PC experience streamed from the Microsoft Cloud to any device, AutoPatch simplifies the crucial task of keeping these virtual environments secure and up-to-date, particularly for the supported Enterprise edition.
It's important to verify your specific Windows 365 subscription, as this directly impacts Autopatch compatibility; access to Autopatch's automated update management for these Cloud PCs is included with Windows 365 Enterprise subscriptions, but not with Business subscriptions.
NOTE: Windows Autopatch is not available for Windows 365 Business; it supports Windows 365 Enterprise only.
Autopatch is included with the following Microsoft 365 subscriptions:
These licenses encompass the necessary Windows 10/11 editions:
Before enrolling devices in Windows Autopatch, ensure the following conditions are met:
Once you’ve met these requirements, refer to Microsoft’s guidance for deploying Windows Autopatch in your organization.
Autopatch simplifies update management by automating the deployment process, reducing manual intervention, and minimizing disruptions. To understand its advantages, it's helpful to compare it with traditional update management methods like Windows Update for Business (WUfB), Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), and Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM).
| Capability | Windows Autopatch | Windows Update for Business (WUfB) | Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Update Automation | Fully automated; Microsoft manages update deployment, monitoring, and rollback processes. | Admins define update policies; devices fetch updates directly from Microsoft Update. | Admins manually approve and deploy updates; requires on-premises infrastructure. | Admins have full control over update deployment; supports complex scenarios; requires significant infrastructure. |
| Deployment Rings | Utilizes predefined rings (Test, First, Fast, Broad) to gradually deploy updates and monitor impact. | Admins can configure deployment rings with custom deferral periods. | Not inherently supported; admins must manually create groups and schedules. | Supports phased deployments through custom collections and maintenance windows. |
| Management Tool | Managed through Microsoft Intune; no additional infrastructure required. | Managed via Microsoft Intune or Group Policy; no additional infrastructure required. | Managed via WSUS console; requires on-premises servers and configuration. | Managed through Configuration Manager console; requires on-premises servers and configuration. |
| Reporting and Monitoring | Provides detailed reporting through Intune, including update compliance and device health metrics. | Offers basic reporting capabilities; more advanced reporting requires additional tools. | Provides limited reporting; more detailed insights require integration with other tools. | Offers comprehensive reporting and analytics; supports integration with other Microsoft tools. |
| Licensing Requirements | Included with Microsoft 365 Business Premium, F3, E3, E5, A3, and A5 licenses. | Available with Windows 10/11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. | No specific licensing requirements; available with supported Windows Server editions. | Requires appropriate Configuration Manager licensing; often used in enterprise environments. |
| Ideal Use Case | Organizations seeking a hands-off, automated update management solution with minimal administrative overhead. | Organizations desiring control over update deployment timing without managing infrastructure. | Organizations needing granular control over updates and operating in environments with strict compliance requirements. | Large enterprises requiring comprehensive management of updates, applications, and devices across complex environments. |
While Windows Autopatch offers streamlined update management, it's important to be aware of its limitations and considerations to ensure it aligns with your organization's needs.
| Category | Limitation or Consideration | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Device Requirements | Entra ID or hybrid join required | On-premises domain-joined devices are not supported |
| Must be managed by Intune or co-managed with Configuration Manager | Devices must check in with Intune every 28 days | |
| Windows 365 Business not supported | Only Windows 365 Enterprise is supported | |
| Licensing Constraints | Limited to select Microsoft 365 plans | Supported: Business Premium, F3, E3, E5, A3, A5 |
| Not available for Government Cloud (GCC) customers | GCC, GCC High, and DoD tenants are not supported | |
| Configuration Issues | Conflicts with Group Policy, Configuration Manager, or local settings can impact functionality | Recommended to remove or adjust conflicting configurations |
| Feature Limitations | No support for on-prem domain-joined devices | Devices must be cloud-managed or hybrid-joined |
| Limited availability of features in some environments | Certain Autopatch capabilities may not work outside commercial tenants |
Nerdio enhances your organization's use of Windows Autopatch by providing tools that automate and simplify patch management across your IT environment. Through Nerdio Manager for Enterprise, you can streamline update processes, reduce administrative overhead, and maintain compliance with ease.
Nerdio Manager for Enterprise offers features that automate and manage Windows updates effectively:
Automated Patching for Desktop Images and Session Hosts: Schedule and manage Windows patching on desktop images and session hosts to ensure timely updates.
Scripted Actions: Utilize built-in scripts to automate routine tasks, reducing manual intervention.
Compliance Reporting: Access detailed reports to monitor update compliance across your devices.
Integration with Microsoft Intune: Manage updates and device configurations seamlessly within your existing Intune environment.
Windows Autopatch offers a streamlined, automated approach to managing updates for Windows and Microsoft 365 applications. However, determining if it's the right fit for your organization depends on specific factors like licensing, device management infrastructure, and operational requirements.
To evaluate the suitability of Windows Autopatch for your organization, consider the following criteria:
Licensing and Eligibility:
Device Management Infrastructure:
Operational Considerations:
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Licensing | Microsoft 365 Business Premium, F3, E3, E5, A3, or A5 |
| Device Join Type | Microsoft Entra ID joined or hybrid joined |
| Management Tool | Microsoft Intune (standalone or co-managed) |
| Device Ownership | Corporate-owned devices only |
| Government Cloud Support | Not supported for GCC customers |
Yes, Windows Autopatch is included at no additional cost with eligible Microsoft 365 subscriptions, such as Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 or higher.
To change Windows Update settings from automatic to manual, you can use the Group Policy Editor:
Press Win + R, type gpedit.msc, and press Enter.
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update.
Double-click on Configure Automatic Updates.
Select Disabled or configure as desired, then click OK.
This method is available on Windows 10/11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
You can adjust Windows Update settings through the Settings app:
Open Settings from the Start menu.
Click on Update & Security, then select Windows Update.
Click on Advanced options to modify update preferences, such as pausing updates or choosing update channels.
Windows Autopatch is a cloud-based service that automates the deployment of updates for Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams. It aims to enhance security and productivity by ensuring devices are up to date without manual intervention.
Windows Autopatch offers automated update management, reducing the administrative burden on IT departments. It ensures timely deployment of updates, which can enhance security and system stability. However, its suitability depends on your organization's specific needs and infrastructure.

Carisa Stinger
Head of Product Marketing
Carisa Stringer is the Head of Product Marketing at Nerdio, where she leads the strategy and execution of go-to-market plans for the company’s enterprise and managed service provider solutions. She joined Nerdio in 2025, bringing 20+ years of experience in end user computing, desktops-as-a-service, and Microsoft technologies. Prior to her current role, Carisa held key product marketing positions at Citrix and Anthology, where she contributed to innovative go-to-market initiatives. Her career reflects a strong track record in driving growth and adoption in the enterprise technology sector. Carisa holds a Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology.