Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
This guide provides an objective overview of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), including how it works, key benefits, challenges, use cases, and comparisons.
This guide provides an objective overview of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), including how it works, key benefits, challenges, use cases, and comparisons.
Carisa Stinger | May 21, 2025
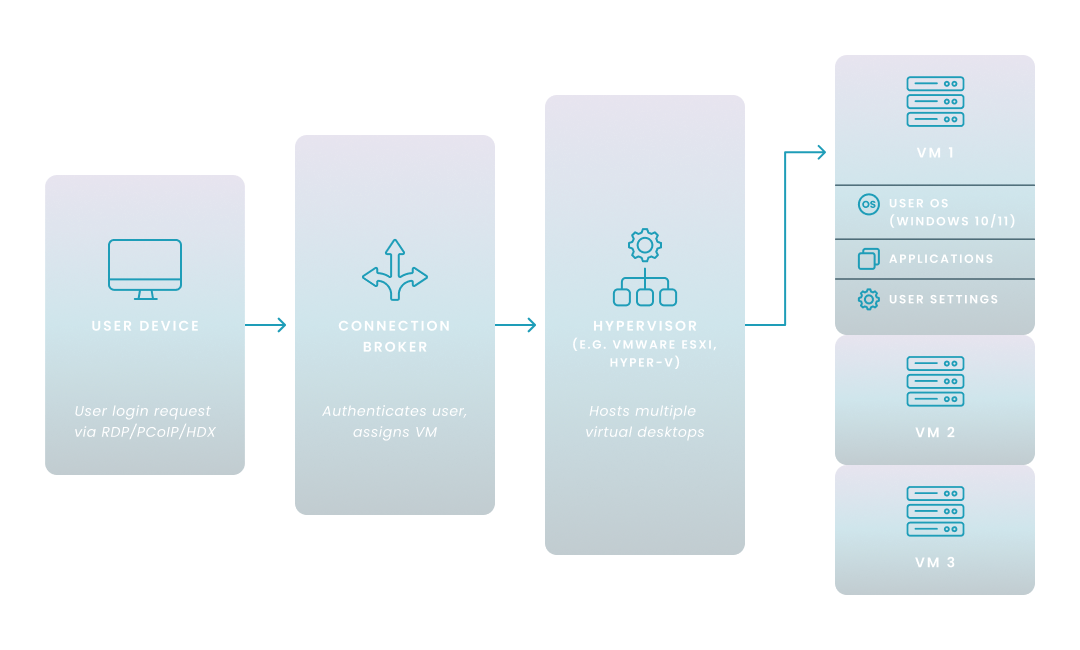
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that hosts desktop environments on centralized servers and delivers them to end users over a network. Instead of running the operating system and applications locally, users access a virtual desktop from nearly any device—whether in the office, at home, or on the go. This setup gives you centralized control over desktops, improves data security, and simplifies IT management.
VDI can help reduce hardware costs, support remote work strategies, and ensure a consistent experience for your users. It’s especially useful for organizations that need to manage large numbers of desktops efficiently, securely, and at scale.
VDI delivers desktop environments from a centralized server to endpoint devices over a network. When a user logs in, they connect to a virtual machine (VM) hosted in your data center or cloud environment.
The choice between persistent and non-persistent VDI impacts both user experience and IT management. Here’s a table to help you decide what best fits your needs:
| Persistent VDI | Non-persistent VDI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Each user has a dedicated VM with a unique desktop that saves settings, files, and changes between sessions. | Users are assigned a generic VM that resets after logout—no data or settings are saved. |
| Best For | Power users or those who need customization. | Task workers, call centers, or kiosk environments. |
| Pros | Personalized experience, supports application installs and custom settings. | Easier to manage, ideal for large user pools with similar needs. |
| Cons | Higher storage and management overhead. | No data persistence; users need separate storage for files. |
When evaluating desktop virtualization options, it's essential to understand how Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) differs from other solutions like Desktop as a Service (DaaS) and Remote Desktop Services (RDS). Each offers unique benefits and trade-offs in terms of management, cost, scalability, and user experience.
While both VDI and DaaS deliver virtual desktops to end users, they differ primarily in infrastructure ownership and management responsibility.
Examples of VDI software and solutions include platforms like VMware Horizon, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, and Oracle Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. While established solutions like Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops exist, many organizations actively investigate Citrix alternatives, particularly when comparing DaaS offerings, to find solutions that may offer more favorable cost structures, simplified management, or tighter integration with their chosen cloud platform.
Additionally, Microsoft offers Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD), which is a Desktop as a Service (DaaS) solution on the cloud service Azure, and Windows 365, a cloud-based PC service; while these are not strictly traditional VDI software, they provide similar virtualized desktop experiences. Another approach for leveraging Microsoft's cloud is running Citrix on Azure, which enables businesses to host their Citrix virtual app and desktop workloads in Azure, thereby gaining cloud flexibility and scalability while maintaining their familiar Citrix management plane.
| Category | VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) | DaaS (Desktop as a Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | You own and manage the infrastructure (servers, storage, networking). | Hosted and managed by a third-party service provider. |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront CapEx for hardware and licenses; ongoing maintenance costs. | Subscription-based OpEx model; more predictable monthly costs. |
| Scalability | Limited by available on-prem resources; scaling requires hardware investment. | Easily scalable; resources can be adjusted on demand via the cloud. |
| IT Management | Requires in-house expertise for setup, updates, and troubleshooting. | Provider handles infrastructure management, updates, and maintenance. |
VDI and Remote Desktop Services (RDS) are both Microsoft technologies that provide remote desktop access, but they differ in architecture and user experience.
| Category | VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) | RDS (Remote Desktop Services) |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Each user gets a dedicated virtual machine running a desktop OS (e.g., Windows 10/11). | Multiple users share sessions on a single server running a server OS (e.g., Windows Server). |
| User Experience | Personalized desktop experience with full isolation between users. | Shared session environment with limited personalization. |
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated resources per user; more consistent performance. | Shared resources; performance can vary based on user load. |
| Cost | Higher infrastructure and licensing costs due to per-user VMs. | More cost-effective; fewer resources and licenses needed per user. |
VDI offers several strategic advantages that can help you improve IT efficiency, support a distributed workforce, and strengthen your organization’s security posture. Below are some of the most commonly cited and verifiable benefits for enterprise environments.
With VDI, desktops and data are hosted in your data center or a secure cloud environment—not on local devices. This centralized model helps reduce the risks associated with data loss or theft.
VDI centralizes control, making it easier for your IT team to manage desktops, deploy applications, and maintain systems from a single location.
VDI can reduce some infrastructure and operational costs, particularly over time and at scale. While initial setup can be capital-intensive, centralized management and extended hardware lifespans can deliver long-term savings.
The table below compares traditional desktops and VDI in terms of both cost and operational efficiency:
| Category | Traditional Desktops | VDI |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Costs | High-performance endpoints required for each user. | Lower-cost endpoints (e.g., thin clients, reused devices) reduce capital spend. |
| Refresh Cycles | 3–5 years; devices must be regularly replaced to maintain performance. | Longer lifespan for endpoints; most processing happens on the server side. |
| IT Support Effort | Local troubleshooting for each device increases overhead. | Centralized control simplifies updates, patching, and provisioning. |
| Energy Consumption | High, due to many distributed, full-power devices. | Lower, especially with thin clients and centralized infrastructure optimization. |
| Software Licensing | OS and application licenses needed for every endpoint. | Shared licensing models possible; centralized licensing can reduce duplication. |
| Security Management | Varies by device; harder to enforce consistent policies. | Centralized security policies reduce risk and simplify compliance. |
| Deployment Speed | Manual setup per device can be time-consuming. | Rapid provisioning from golden images accelerates deployment. |
| Disaster Recovery | Device failure may result in data loss without backups. | Centralized storage simplifies backup, replication, and recovery. |
VDI enables secure access to enterprise desktops from virtually any device, making it ideal for remote access or hybrid workforces and BYOD (bring your own device) environments.
While VDI offers significant benefits, implementing it at scale involves several technical and operational considerations. Understanding these challenges up front can help you plan effectively and avoid costly missteps.
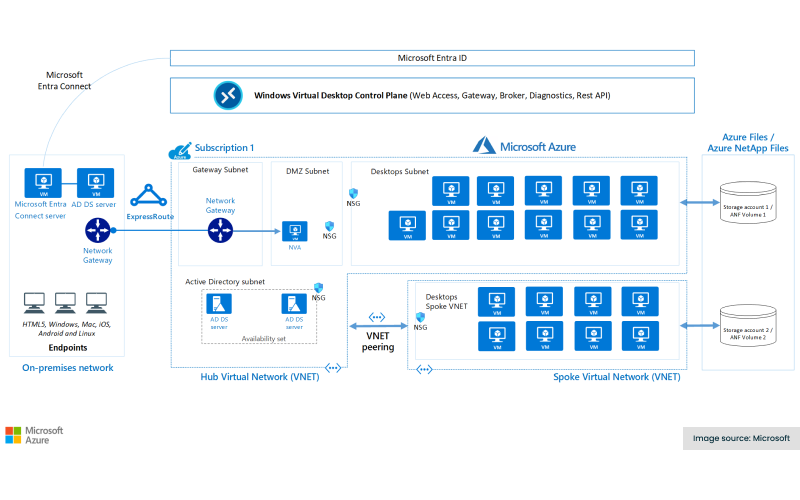
The above diagram shows a typical architectural setup for Azure Virtual Desktop. As you can see, deploying VDI typically requires significant planning and infrastructure investment. You'll need to architect a solution that aligns with your performance, security, and user requirements.
User satisfaction depends heavily on consistent desktop performance. Network latency, bandwidth, and back-end resource constraints can all affect responsiveness.
Although VDI can reduce long-term IT operational costs, initial investments are often high and ongoing licensing can be complex.
Scaling VDI effectively means more than just adding users—it involves capacity planning, monitoring, and resource optimization.
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for Windows 365 in your organization.
VDI centralizes desktops and data within your data center or cloud environment, making it easier to enforce security policies and support compliance efforts. By minimizing the use of local storage and enabling consistent controls, VDI helps reduce risk and improve visibility.
VDI allows your IT team to manage all virtual desktops from a central location, ensuring consistent policy enforcement across your organization.
With VDI, sensitive data stays within the secure perimeter of your data center or cloud—not on user devices—reducing the attack surface.
Choosing the right VDI solution depends on your organization’s technical requirements, existing infrastructure, and long-term goals. When selecting a VDI solution, it's vital to consider how it aligns with your organization's overall end user computing (EUC) strategy, which focuses on providing employees secure and seamless access to their digital workspace, regardless of device or location, to maximize productivity.
Start by assessing whether the VDI platform integrates smoothly with your current systems—both hardware and software.
A good VDI solution should scale easily as your user base grows or your workload changes.
VDI pricing can vary significantly depending on deployment type and vendor licensing. Understanding total cost of ownership is critical.
Long-term success with VDI often depends on the strength of vendor support and the surrounding ecosystem.
Nerdio assists enterprises in implementing Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) by providing a comprehensive platform that simplifies deployment, enhances management, and optimizes costs. Through its suite of tools, Nerdio enables organizations to efficiently transition to and maintain scalable, secure virtual desktop environments.
Nerdio streamlines the VDI deployment process, reducing the complexity and time traditionally associated with setting up virtual desktops.
Nerdio provides features that help organizations manage and reduce the costs associated with VDI implementations.
| Cost Optimization Area | Traditional VDI (Typical Practice & Cost Impact) | Nerdio-Optimized VDI (Feature & Saving*) |
|---|---|---|
| Compute right-sizing & auto-scaling | Static sizing; admins often over-provision virtual desktops to cover peak demand, paying for idle capacity. | Nerdio’s policy-based auto-scaling starts, stops, creates or deletes VMs in real time. Customers typically cut Azure compute and storage spend by 50–70%. |
| Session-host OS-disk tiering | Premium SSD (or similar) disks stay attached 24/7—even while VMs are powered off—incurring full storage charges. | Auto-scale dynamically downgrades powered-off OS disks to inexpensive tiers and re-upgrades at boot, delivering up to 75% storage cost savings. |
| Reserved Instance & Azure Hybrid Benefit utilisation | RI sizing is manual; PAYG pricing is common. Hybrid Benefit is frequently under-used, so organisations miss bulk discounts. | Nerdio analyses usage patterns and recommends RIs; it tracks coverage and alerts on shortfalls. A 1-year RI typically saves ≈ 40%, a 3-year RI ≈ 60%, and combining a 3-year RI with Azure Hybrid Benefit can reach ≈ 80% vs. PAYG. Learn more. |
| License right-sizing & analytics | Licences (Windows 365, AVD user CALs, etc.) are often assigned manually; unused licences accumulate. | Nerdio uses AI-powered licence recommendations and usage analytics in Manager for Enterprise v7 to highlight under-utilised licences and suggest cheaper SKUs—helping avoid unnecessary spend. |
Nerdio's platform is designed to accommodate the evolving needs of enterprises, ensuring that VDI environments can scale effectively.
Nerdio enhances the security posture of VDI environments and aids in meeting compliance requirements.
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) is a technology that hosts desktop operating systems on a central server, allowing users to access them remotely. A VM (Virtual Machine) is a software emulation of a physical computer, and VDI relies on VMs to deliver those desktops, but a single server hosts many VMs in a VDI setup, whereas a VM can exist independently.
VDI delivers a complete desktop environment to the user's device, so applications and data reside on the server. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure connection to a network, allowing users to access resources as if they were on that network, but applications run on the user's device.
There are primarily two types: persistent and non-persistent. Persistent VDI assigns users to a dedicated desktop image that they can customize and retains settings between sessions. Non-persistent VDI provides users with a fresh, generic desktop each time they log in, often used for task workers.
VDI is used to enhance security by centralizing data, support remote work by enabling access from any device, and improve manageability by simplifying desktop administration. It's common in industries with strict compliance needs (healthcare, finance), organizations with BYOD policies, and scenarios requiring consistent desktop experiences.




Carisa Stinger
Head of Product Marketing
Carisa Stringer is the Head of Product Marketing at Nerdio, where she leads the strategy and execution of go-to-market plans for the company’s enterprise and managed service provider solutions. She joined Nerdio in 2025, bringing 20+ years of experience in end user computing, desktops-as-a-service, and Microsoft technologies. Prior to her current role, Carisa held key product marketing positions at Citrix and Anthology, where she contributed to innovative go-to-market initiatives. Her career reflects a strong track record in driving growth and adoption in the enterprise technology sector. Carisa holds a Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology.