Connect to Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
This guide walks you through the process of connecting to AVD: using different connection methods, troubleshooting, and how to reduce complexity and cost.
This guide walks you through the process of connecting to AVD: using different connection methods, troubleshooting, and how to reduce complexity and cost.
Amol Dalvi | May 2, 2025
Azure Virtual Desktop offers flexible connection options, allowing you to access your workspace from various devices and operating systems.
The Azure portal streamlines these tasks, while other methods offer flexibility. When creating a host pool, choose between session host configuration (preview) for a managed approach or standard management for custom control.
We also discuss how third-party tools provide automation, optimization, and streamlined management capabilities to accelerate AVD deployment, minimize costs, and reduce complexity.
To connect to Azure Virtual Desktop, choose the section below that matches the operating system or device you're using:
NOTE: For a seamless and secure connection to devices and apps across Azure Virtual Desktop, Windows 365, and Microsoft Dev Box, we encourage you to download Windows App.
Before you connect to Azure Virtual Desktop from your Windows device, ensure you have the following:
1) Launch the Remote Desktop app from your Start Menu.
2) Subscribe to a workspace:
3) Connect to your desktops and applications:
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for AVD in your organization.
Before you connect to Azure Virtual Desktop from your macOS device, ensure you have the following:
1) Launch the Microsoft Remote Desktop application from your Applications folder.
2) Add a workspace:
3) Connect to your desktops and applications:
Before you connect to Azure Virtual Desktop from your iOS or iPadOS device, ensure you have the following:
1) Launch the Microsoft Remote Desktop application from your home screen.
2) Add a workspace:
3) Connect to your desktops and applications:
Before you connect to Azure Virtual Desktop from your Android or Chrome OS device, ensure you have the following:
1) Launch the Microsoft Remote Desktop application from your app drawer.
2) Add a workspace:
3) Connect to your desktops and applications:
Before you connect to Azure Virtual Desktop through a web browser, ensure you have the following:
NOTE: If you are currently logged in to your browser with a Microsoft Entra account that’s different from the one you want to use for remote access to AVP, either sign out first or use a private browser window.
1) Access the AVD web client: Open your web browser and navigate to the Azure Virtual Desktop web client.
2) Sign in:
3) Connect to your desktops and applications:
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for AVD in your organization.
Now that you know how to connect to Azure Virtual Desktop, let's explore the key components that make up your AVD environment.
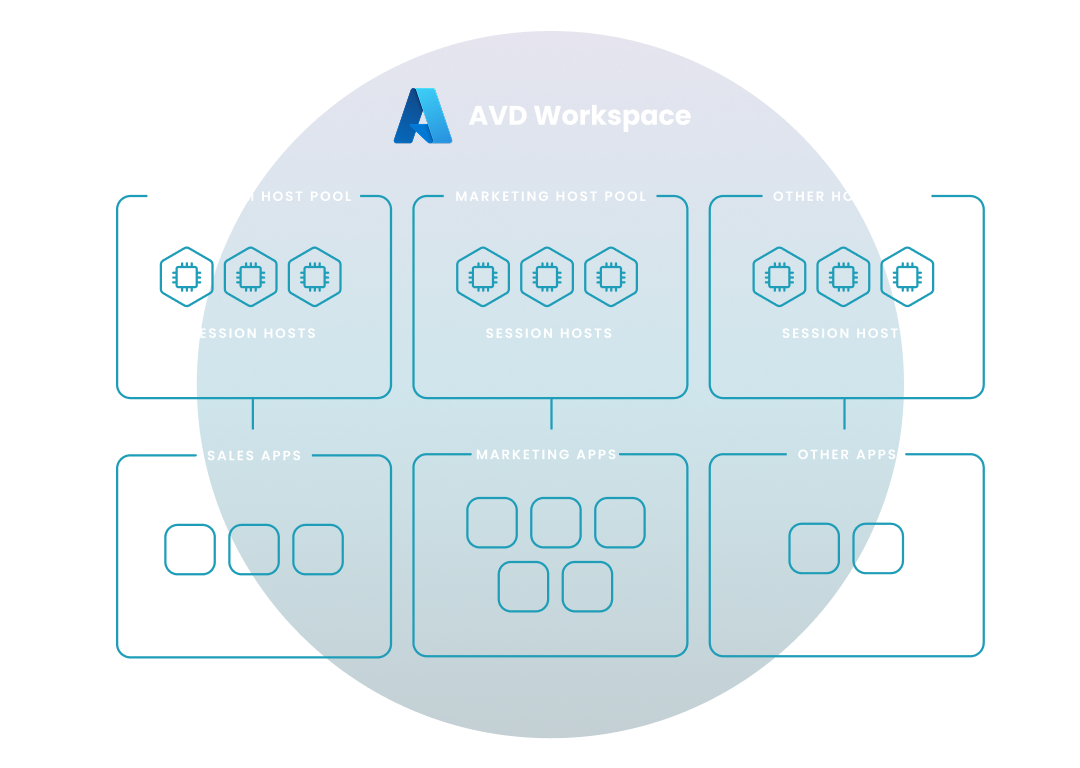
In Azure Virtual Desktop, a workspace is a collection of desktops and applications that are made available to users. Think of it as a container that organizes your virtual resources. Your organization might have a single workspace for all users or multiple ones tailored to different departments or teams.
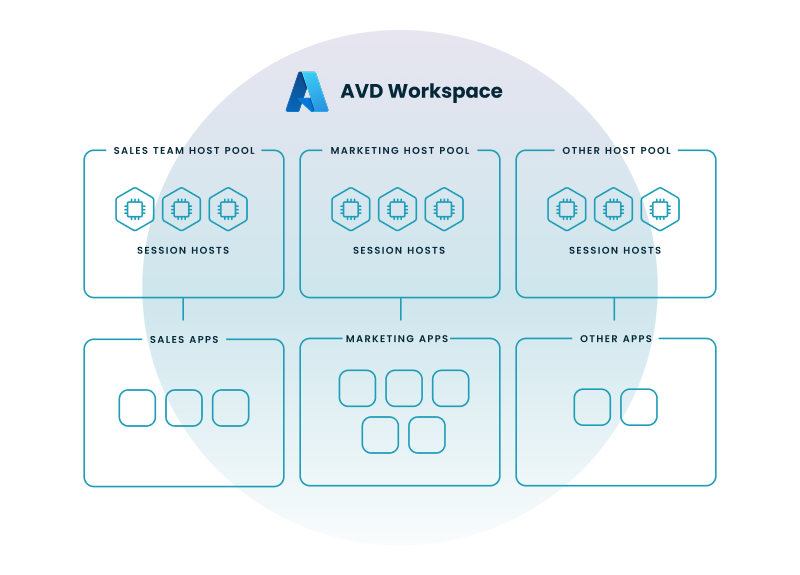
Here are some essential components within an AVD workspace:
Host Pools: A host pool is a collection of virtual machines (VMs) that run your desktops and applications. These VMs are hosted in Azure and provide the computing power for your AVD environment.
App Groups: App groups determine which applications are available to users within a workspace. You can create different app groups for different user groups, ensuring that people only have access to the applications they need.
Session Hosts: Session hosts are the individual VMs within a host pool that users connect to. When you launch a desktop or application in AVD, you're connecting to a session host.
Azure Virtual Desktop offers robust security features to protect your data and ensure that only authorized users can access your workspace.
AVD supports various authentication methods, including:
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): The most common method, using your organization's Azure AD credentials to verify your identity.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from a mobile app or a fingerprint scan.
Third-party identity providers: Integrate with other identity providers for seamless access to AVD.
Here are some security best practices for AVD:
Enable MFA: Enforce MFA for all users to prevent unauthorized access.
Regularly update clients: Keep your Remote Desktop clients and web browsers updated to benefit from the latest security patches.
Control access: Use app groups and role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data and applications.
Monitor activity: Monitor AVD activity logs to detect and respond to suspicious behavior.
While Azure Virtual Desktop is designed for a smooth and reliable experience, you might occasionally encounter connection issues. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
Network connectivity: Slow or intermittent internet connection can lead to poor performance or connection failures.
Authentication errors: Incorrect credentials or issues with Azure AD authentication can prevent you from connecting.
Display issues: Screen resolution problems or black screens can occur due to graphics settings or driver compatibility.
Application errors: Specific applications might fail to launch or function correctly within the AVD environment.
Check your internet connection: Ensure you have a stable internet connection with sufficient bandwidth.
Verify your credentials: Double-check that you're using the correct username and password for your Azure AD account.
Update your client: Make sure you're using the latest version of the Remote Desktop client or web browser.
Adjust display settings: Try adjusting the display resolution or scaling settings within the AVD session.
Consult documentation: Refer to the official Microsoft documentation for specific error messages or troubleshooting guides.
While Azure Virtual Desktop offers a powerful platform for delivering virtual desktops and applications, managing and optimizing your AVD environment can be complex. This is where Nerdio comes in.
Nerdio provides a comprehensive suite of solutions designed to simplify and optimize AVD deployment and management. Here's how Nerdio can help:
Simplified deployment: Streamline the process of deploying and configuring AVD, reducing the time and effort required to get started.
Automated management: Automate routine tasks such as scaling resources, patching VMs, and managing user access, freeing up your IT team.
Cost optimization: Optimize your AVD costs by automatically scaling resources based on demand and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
Enhanced security: Strengthen your AVD security posture with advanced features like multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and activity monitoring.
With Nerdio, you can unlock the full potential of Azure Virtual Desktop while reducing complexity and costs.
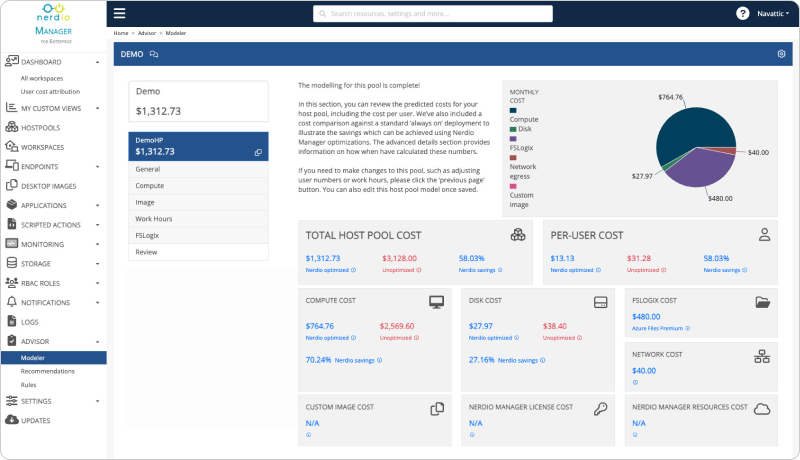
See this demo to discover how you can simplify operations, enhance security, and lower the total Azure cost of your entire Windows 365 or AVD environment with Nerdio Manager.
See how you can optimize processes, improve security, increase reliability, and save up to 70% on Microsoft Azure costs.
To connect to your Azure virtual desktop, you'll first need to download and install the Microsoft Remote Desktop client on your device (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android). Then, subscribe to your organization's Azure Virtual Desktop workspace using your credentials and double-click on the desired desktop or application to launch a session.
Users can access Azure Virtual Desktop through various methods, including the Microsoft Remote Desktop client, a web browser, or a mobile app. The specific method depends on the user's device and operating system.
Connecting to a virtual desktop typically involves using a remote desktop client application and providing the necessary credentials, such as a username and password, or a connection URL. The client establishes a connection to the virtual desktop environment, allowing you to interact with it as if you were sitting in front of a physical computer.
To log in to VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure), you'll typically use your organization's provided credentials, such as your username and password. You might also need to provide additional authentication factors, such as a one-time code or a security token, depending on your organization's security policies.
Joining an Azure Virtual Desktop domain typically involves configuring your virtual machine (VM) to join your organization's Active Directory domain. This process usually requires providing domain administrator credentials and configuring DNS settings to allow the VM to communicate with the domain controller.



Nerdio Manager for Enterprise
Software product executive and Head of Product at Nerdio, with 15+ years leading engineering teams and 9+ years growing a successful software startup to 20+ employees. A 3x startup founder and angel investor, with deep expertise in Microsoft full stack development, cloud, and SaaS. Patent holder, Certified Scrum Master, and agile product leader.