Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
This guide provides practical advice on deploying and managing an Azure Virtual Desktop environment, helping you optimize costs and improve performance.
This guide provides practical advice on deploying and managing an Azure Virtual Desktop environment, helping you optimize costs and improve performance.
Amol Dalvi | May 1, 2025
Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is a comprehensive cloud-based desktop and app virtualization service designed to give your organization secure, flexible remote work. Built on the Microsoft Azure platform, AVD enables you to provide your employees with personalized, scalable virtual desktops and applications accessible from anywhere.
Key benefits for your enterprise include cost efficiency with a pay-as-you-go model, robust security with Azure’s built-in protections, simplified IT management, and seamless integration with Microsoft 365 and Teams for enhanced productivity.
Azure Virtual Desktop offers a powerful solution for you to modernize your IT infrastructure, enhance workforce productivity, and optimize costs. Designed to deliver secure, scalable, and flexible virtual desktop experiences, AVD addresses the unique needs of large organizations, from supporting remote and hybrid teams to enabling seamless application delivery.
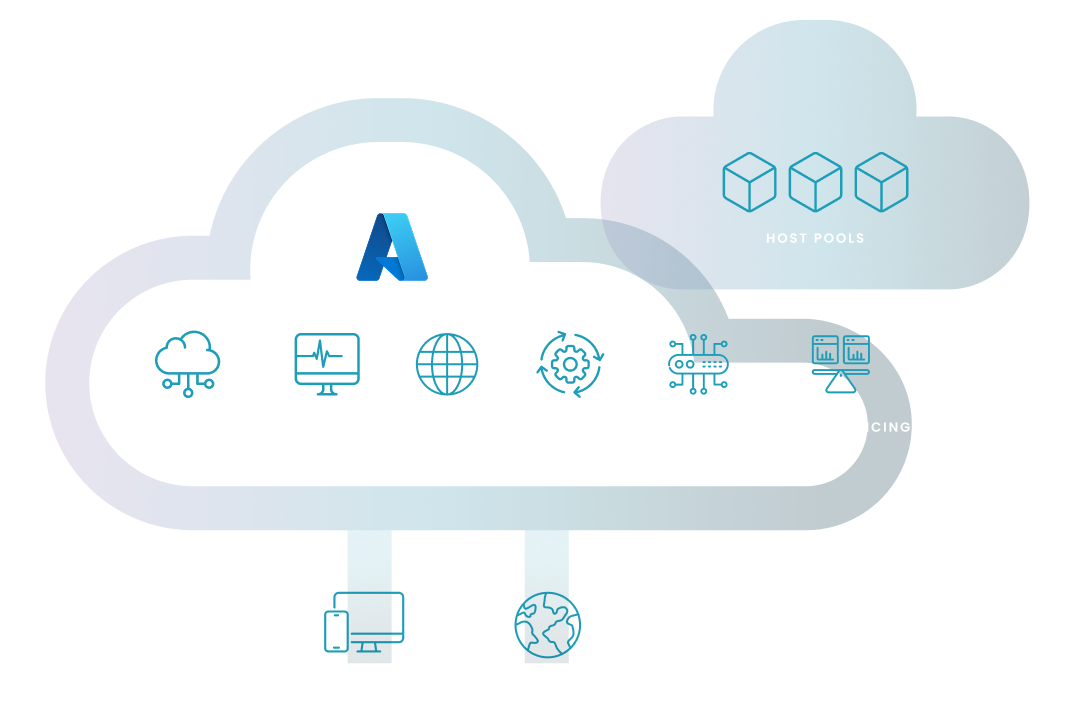
AVD includes the roles that were traditionally managed manually by administrators–such as Web access, diagnostics, broker, management, gateway, and load balancing–all as a scalable managed service on Azure. And you can provision the compute and configure user experiences for host pools based on your specific needs. Host pools are collections of virtual machines configured to deliver desktop and app experiences to users, enabling flexible and scalable resource allocation. Plus, it works with full-featured apps across any device–Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android–and from any location.
Below, we explore in more detail the key benefits that make Azure Virtual Desktop a compelling choice for enterprises.
You can configure virtual machines that deliver Windows 11 and Windows 10 application and desktop experiences with these benefits:
You can also deploy infrastructure in secure Azure regions worldwide and analyze connection quality. This gives you:
For a seamless user experience, you can enable access to Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows Server versions (2022, 2019, 2016).
Centrally managing your virtual desktops reduces IT complexity and ensures resilience.
Tools like Azure Private Link and RDP Shortpath help you enhance security and reliability.
Use advanced tools such as custom image templates to efficiently manage large-scale deployments.
Windows 11 and Windows 10 multi-session functionality allows you to have multiple users on a single virtual machine.
Transitioning from on-premises solutions to Azure Virtual Desktop helps you to reduce infrastructure and licensing expenses.
You pay only for the compute capacity you use, with no upfront payments or long-term commitments.
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for AVD in your organization.
Let's walk through a simplified overview of the core components of Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) and how they interact.
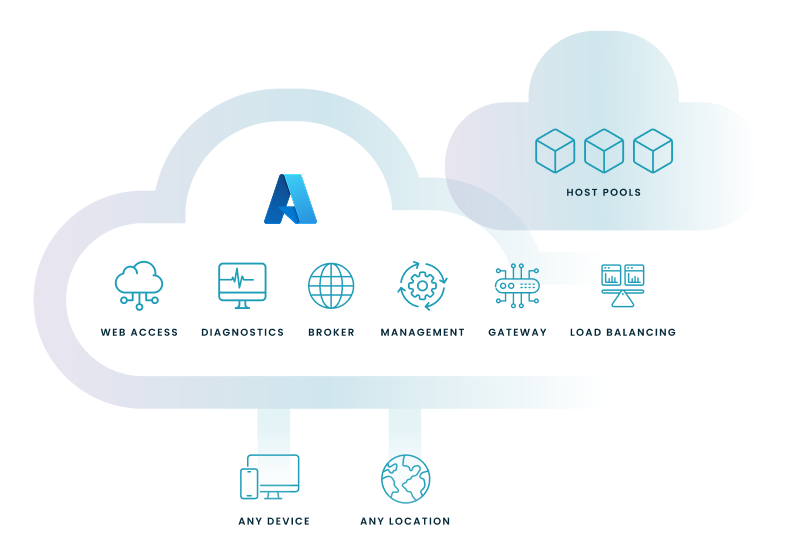
Here's an explanation of the diagram:
In this section, we explore key use cases where AVD delivers value for your enterprise, from enhancing business continuity to optimizing secure application delivery.
This step-by-step wizard tool gives you the total cost of ownership for AVD in your organization.
Here we help you understand how to manage and optimize costs while transitioning to Azure Virtual Desktop, highlighting its financial advantages over traditional virtualization platforms. Below is an overview of pricing models:
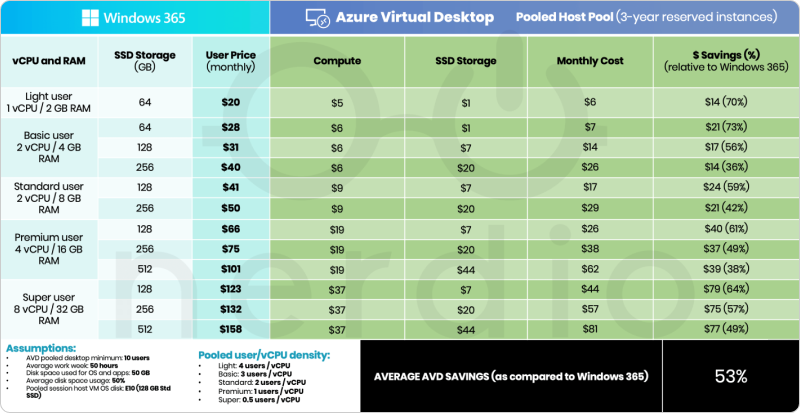
As you can see in the table above, here are the key differences:
DIVE DEEPER: Azure Virtual Desktop Pricing Guide
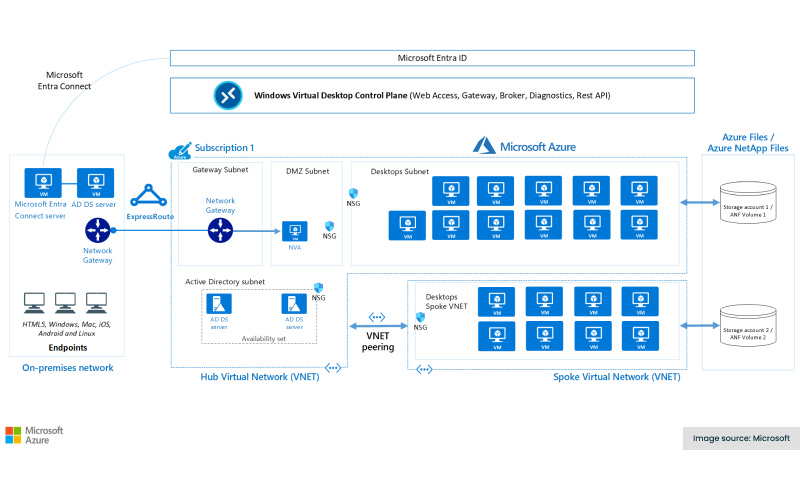
This architectural diagram shows how AVD is typically employed as part of a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) at enterprise scale.
The step-by-step guide below gives you a clear roadmap for deploying Azure Virtual Desktop, leveraging Microsoft’s resources, and utilizing third-party tools for seamless implementation and management.
Azure Virtual Desktop is a fully managed desktop virtualization service that provides secure, multi-user access to virtualized Windows desktops and apps, optimized for scalability and cost efficiency. Virtual Machines (VMs), on the other hand, are individual compute resources that require more manual setup and management, offering greater customization for various workloads but without the desktop-focused features of AVD.
Azure Virtual Desktop and Citrix both provide virtualization solutions for delivering remote desktops and applications, but AVD is a fully managed service from Microsoft, while Citrix offers additional advanced management, customization, and multi-cloud capabilities. AVD can function as a standalone solution or complement existing Citrix deployments, simplifying infrastructure and reducing costs. For enterprises evaluating robust and flexible alternatives to Citrix DaaS, it offers a compelling cloud-native solution with simplified management and cost optimization.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is an on-premises solution that requires managing your own infrastructure, including servers and licenses, to deliver remote desktops and applications. Azure Virtual Desktop, on the other hand, is a cloud-based service managed by Microsoft, offering enhanced scalability, multi-session Windows 11/10 capabilities, and simplified management without the need for on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud PC, offered through Windows 365, provides a fully dedicated, always-on virtual desktop experience designed for simplicity and fixed pricing. Azure Virtual Desktop, formerly known as Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD), is a more flexible, scalable solution with pay-as-you-go pricing, supporting multi-session capabilities and advanced configurations for diverse business needs.
While Azure Virtual Desktop provides a robust foundation, realizing its full potential requires addressing the operational complexities of large-scale management and cost control. This is where automation platforms like Nerdio Manager for Enterprise add significant value, acting as a force multiplier for your IT team. By layering an intuitive management console over the native AVD environment, you can unlock new levels of efficiency and financial governance.
See this demo to discover how you can simplify operations, enhance security, and lower the total Azure cost of your entire Windows 365 or AVD environment with Nerdio Manager.
See how you can optimize processes, improve security, increase reliability, and save up to 70% on Microsoft Azure costs.
Cloud desktops are hosted entirely on a cloud provider's infrastructure, offering scalability, accessibility from anywhere, and pay-as-you-go pricing. VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) is typically deployed on-premises or in a private data center, requiring businesses to manage and maintain the underlying hardware and software.
"Cloud" is a broad term that refers to delivering computing services like servers, storage, databases, and software over the internet. Azure is Microsoft's specific cloud platform that provides a wide range of cloud services, including computing, analytics, storage, and networking, tailored for businesses and developers.
A virtual machine (VM) is a software-based emulation of a physical computer that runs an operating system and applications, typically hosted on physical servers. The cloud, on the other hand, is a platform that provides on-demand access to computing resources, including VMs, over the internet, enabling scalability and eliminating the need for physical hardware management.
A desktop refers to a physical or virtual computer that provides a localized computing environment for users, typically requiring direct access to its hardware or network. The cloud, however, delivers computing resources, applications, and storage over the internet, enabling access from anywhere without being tied to specific hardware.



Nerdio Manager for Enterprise
Software product executive and Head of Product at Nerdio, with 15+ years leading engineering teams and 9+ years growing a successful software startup to 20+ employees. A 3x startup founder and angel investor, with deep expertise in Microsoft full stack development, cloud, and SaaS. Patent holder, Certified Scrum Master, and agile product leader.