NERDIO GUIDE

On-demand webinar
Beyond a conference — NerdioCon 2026: Learning, networking & unforgettable moments.
Save your spot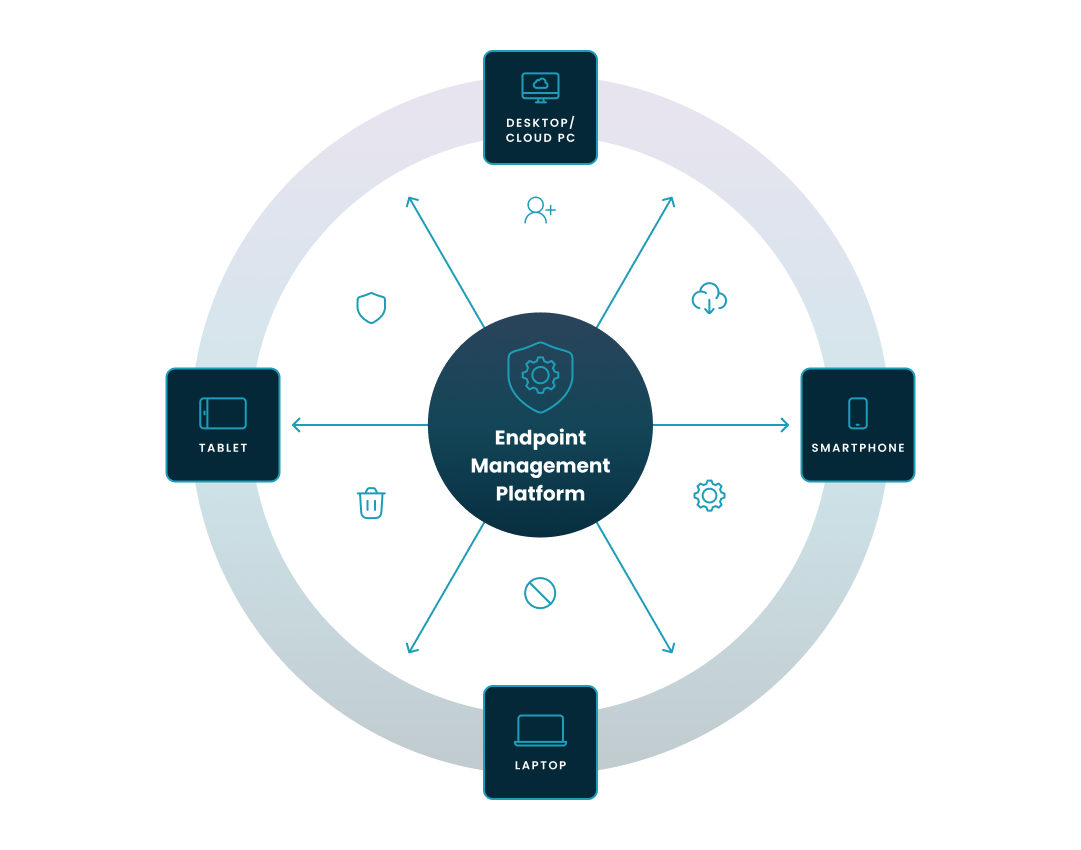
NERDIO GUIDE
Carisa Stringer | November 14, 2025
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a type of security and management software used by IT departments to monitor, secure, and enforce policies on mobile devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Its primary goal is to protect your corporate data and networks while enabling employees to use those devices for work.
This is critical because the "endpoint" is the new perimeter. With remote work and "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD) policies, your data is no longer safe behind a central firewall. Consider that 44-51% of users face mobile scams daily and the human element is involved in 68% of all data breaches. MDM is the foundational technology that allows you to manage this risk, prevent data breaches, and ensure all your organization's devices are compliant and secure.
MDM uses a client-server architecture to give your IT administrators a central way to manage a fleet of devices. It's a straightforward model that allows for large-scale control.
This architecture consists of two main parts: the MDM server and the MDM agent.
The MDM server is the "command center" for your entire mobile fleet. This is a central console—almost always cloud-based today—where your IT team can:
The MDM agent is a small, lightweight software component on the endpoint device (the smartphone, tablet, or laptop). This agent can be a downloaded app or, more commonly, a "profile" installed using the device's built-in management frameworks.
This agent "listens" for commands from the server. When the server sends a command (like "install this app"), the agent uses the device's native Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to execute it. This communication is typically handled by platform-specific push notification services (like the Apple Push Notification service, or APNs), which ensures commands are delivered instantly without draining the device's battery.
While features vary, all enterprise-grade MDM solutions are built on a core set of functionalities. These tools are designed to give you full control over the lifecycle of your corporate devices.
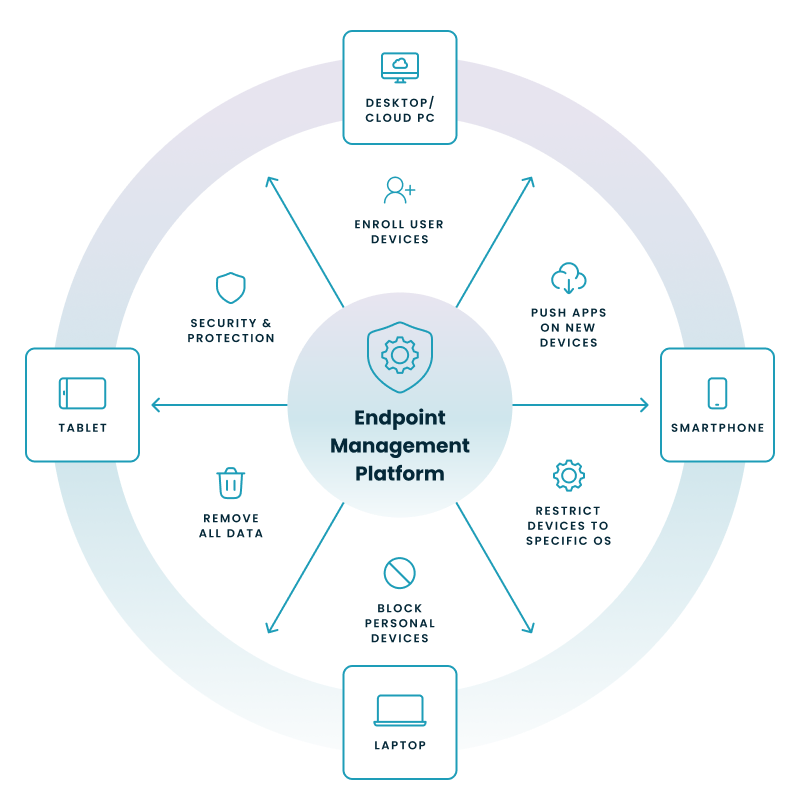
Let's walk through the diagram above.
MDM directly addresses the most significant financial, legal, and operational risks your business faces in a mobile-first world. The value isn't just in security; it's in enabling your business to operate flexibly and efficiently.
When you don't have control over your endpoints, you are exposed to massive risks. Adopting an MDM strategy solves several critical business problems.
A lost or stolen laptop or smartphone is a data breach waiting to happen. The average cost of a data breach in the United. States has hit $10.22 million, and breaches involving remote work cost an average of $131,000 more than those that don't. MDM solves this by giving you the power to remotely lock or wipe that lost device, instantly neutralizing the threat. By enforcing encryption, you ensure that even if the device is stolen, the data on it is unreadable.
Employees want to use their personal phones and laptops for work, but this creates a massive security and privacy headache for IT. MDM solves this through containerization. On an employee's personal device, the MDM can create a separate, encrypted "work profile" or container.
If you operate in an industry like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), or handle European data (GDPR), you face strict regulations on how you protect sensitive information. A lost, unencrypted phone with patient or customer data can lead to staggering fines. HIPAA non-compliance penalties, for example, can range from $141 to $68,928 per violation with an annual cap of $2M.
MDM is a core tool for proving compliance. You can use its reporting features to:
Manually setting up 50 new laptops or phones for new hires is a time-consuming, expensive, and error-prone process. MDM automates this entirely. With "zero-touch" provisioning, a device can be shipped directly to a new employee. When they unbox it and connect to Wi-Fi, the MDM server automatically enrolls it and pushes all the necessary policies, apps, and settings.
This automation transforms IT from a manual repair shop into a strategic operator, saving thousands of hours in labor and getting employees productive on day one.
These terms represent the evolution of endpoint management, and you'll often hear them used interchangeably. MDM was the foundation, but its capabilities grew to meet new business needs, leading to EMM and, finally, UEM.
Today, most modern platforms, including Microsoft's flagship Microsoft Intune, are considered UEM solutions.
Your organization's "endpoints" are no longer just the physical devices you can touch. A modern IT environment is a hybrid of both physical and virtual endpoints.
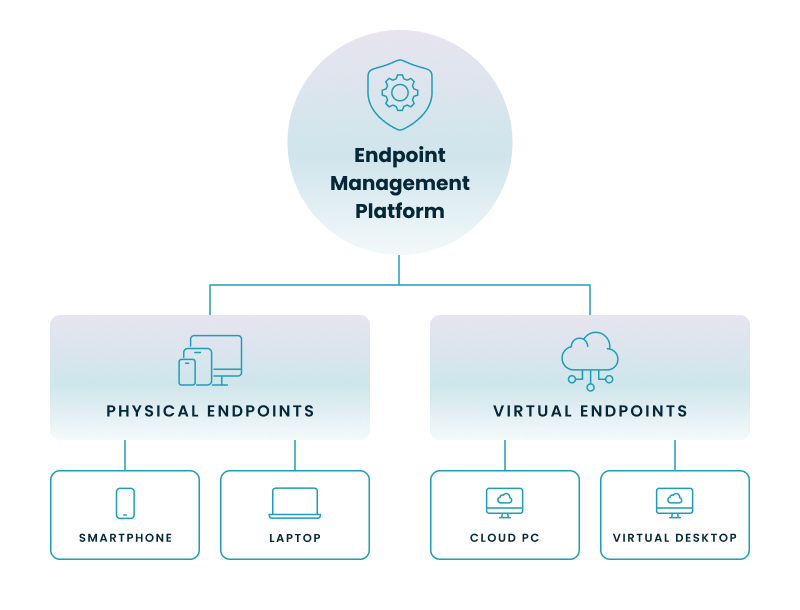
This is a critical management challenge. Your IT team has to manage two separate worlds:
The problem is that traditional UEM tools were built to manage physical hardware. Managing a fleet of virtual desktops—spinning them up, shutting them down to save costs, applying images, and managing user sessions—requires a completely different set of tools and expertise. This leaves IT teams juggling two separate, complex management platforms, one for physical and one for virtual, creating inefficiency and security gaps.
While Microsoft Intune is the native tool for managing endpoints, organizations can face operational challenges when applying its policies at an enterprise scale. Nerdio provides a unified management platform that integrates with and extends Intune to solve these specific challenges, particularly for organizations managing both physical endpoints and virtual desktops like Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) and Windows 365.
Instead of replacing Intune, the platform acts as a simplifying and automation layer that provides a single interface to manage the entire endpoint estate.
Nerdio adds critical functions for enterprises that need to go beyond native Intune capabilities:
The platform unifies management tasks to reduce administrative overhead, cost, and complexity:
By automating and optimizing the most complex parts of endpoint management, Nerdio delivers powerful, measurable results for IT departments.
As Brad Ransbury, Systems Administrator for the City of Corona, noted,
“With Nerdio’s integration with Intune, we now have a real-time view of our devices' security status... We no longer have to dig through multiple screens in Azure or Intune. The information is just there, ready to act on.”
See how you can optimize processes, improve security, increase reliability, and save up to 70% on Microsoft Azure costs.
Yes, an MDM solution can be configured to see browsing history on a corporate-owned device. It gives administrators the technical ability to monitor web traffic, filter content, and log web activity. On personal "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD) phones, this is usually limited to what happens inside a secure "work container" to protect your personal privacy.
If device management is on your phone, it is almost certainly because your employer or school requires it to give you access to secure resources like corporate email, internal apps, or company files. It is the company's way of protecting its data by ensuring your device meets minimum security standards, like having a passcode and being encrypted.
MDM (Mobile Device Management) is a platform for managing the entire device itself—it enforces security rules, pushes apps, and can lock or wipe the phone. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that secures your internet connection by creating an encrypted tunnel, protecting your data from being snooped on while in transit.
A prominent example of a modern MDM platform is Microsoft Intune, which is part of its Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) suite. Other well-known examples include Jamf (which focuses specifically on Apple devices), VMware Workspace ONE, and Kandji.
MDM works on a client-server model. An IT administrator uses a central MDM server (or cloud console) to create and push policies. A small software "agent" or profile on your phone receives these commands and uses the device's built-in management APIs to enforce them, such as requiring a passcode or installing a work app.

On-demand webinar


Carisa Stringer
Head of Product Marketing
Carisa Stringer is the Head of Product Marketing at Nerdio, where she leads the strategy and execution of go-to-market plans for the company’s enterprise and managed service provider solutions. She joined Nerdio in 2025, bringing 20+ years of experience in end user computing, desktops-as-a-service, and Microsoft technologies. Prior to her current role, Carisa held key product marketing positions at Citrix and Anthology, where she contributed to innovative go-to-market initiatives. Her career reflects a strong track record in driving growth and adoption in the enterprise technology sector. Carisa holds a Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology.