7 factors to consider before moving to Microsoft Intune

Table of Contents
Microsoft Intune is a robust, cloud-based endpoint management solution that enables organizations to efficiently manage user access and application delivery across various devices, including mobile, desktop, and virtual endpoints. This comprehensive platform plays a pivotal role in modern IT management strategies, offering a centralized approach to secure device management, application deployment, and compliance enforcement.
Why move to Microsoft Intune?
Intune caters to the needs of the modern mobile workforce by facilitating seamless application delivery and acting as a versatile replacement for SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) and Group Policy Objects (GPOs).
It supports comprehensive mobile device management (MDM) for both company-owned and employee-owned devices, enabling organizations to enforce security policies and ensure compliance across diverse endpoints. It also provides robust security features, including conditional access controls, to protect corporate data and resources.
Another key advantage of Intune is its reporting and compliance capabilities, offering detailed insights into device usage and adherence to organizational policies. By choosing it, organizations can streamline device management, enhance security, and effectively support a mobile workforce, ultimately improving productivity and reducing operational overhead.
Intune is the ideal endpoint management option, but there are elements organizations must be aware of before migrating. Let’s break down seven key factors to consider before making the move.
1. Intune licensing options
The first consideration for organizations moving to Intune is licensing. It offers several licensing plans tailored to meet the diverse needs of its customers. Options include:
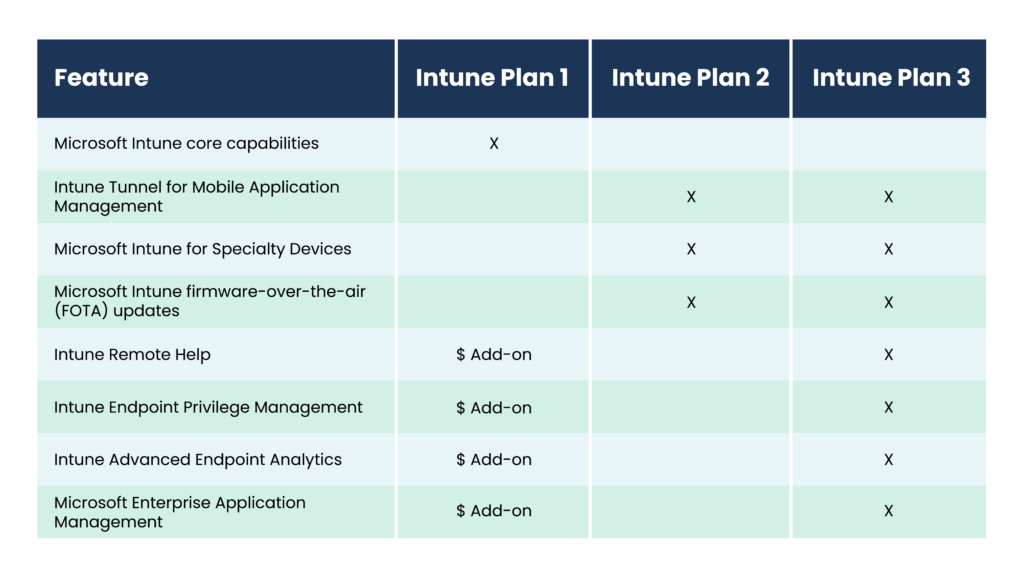
These licensing plans allow organizations to choose the level of functionality and integration that best aligns with their business requirements and IT strategy, providing flexibility and scalability as needs evolve.
You may also want to consider having Microsoft Entra ID Premium licenses to take advantage of automatic enrollment and conditional access policies.
Automatic enrollment is a key feature offered by Entra ID Premium with Intune. It automates the device enrollment process, ensuring that corporate devices are quickly and seamlessly onboarded into the management system without manual intervention.
Conditional access policies are another powerful capability provided by Entra ID Premium and Intune. These policies allow organizations to enforce specific access rules based on various conditions, such as user identity, device health, and location. By implementing conditional access policies, organizations can enhance security and ensure that only trusted devices and users can access corporate resources.
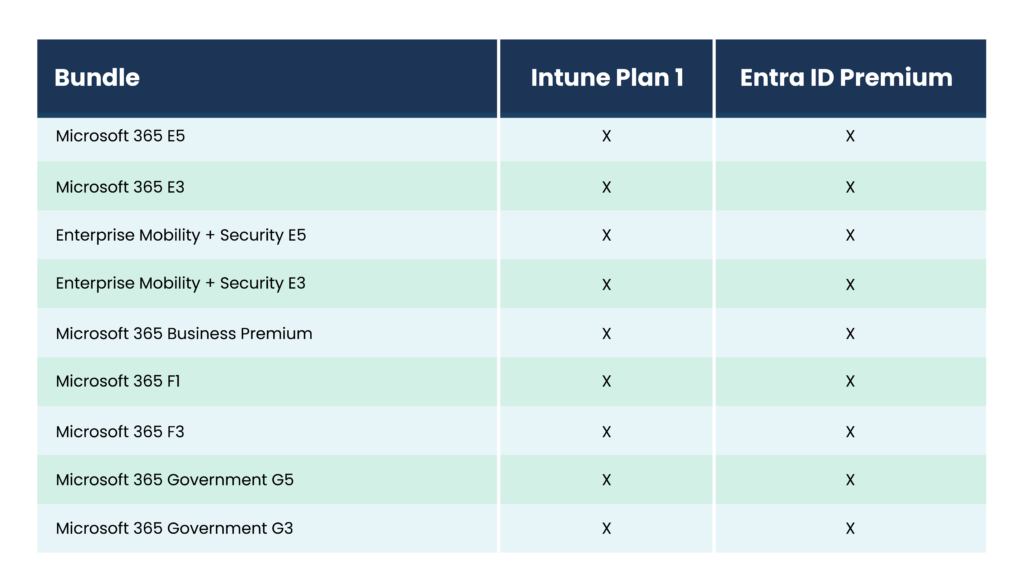
Together, Entra ID Premium and Intune deliver robust device management and security capabilities, streamlining operations and fortifying your organization’s security posture. Luckily, Microsoft loves licensing bundles. Odds are, both solutions are covered in your existing license:
PRO TIP: It’s possible to enable unlicensed admin access, which allows administrators to manage devices and policies without requiring a specific Intune license. To enable this access, navigate to the Microsoft Intune Admin Center, then proceed to Tenant Administration, Roles, and Administrator Licensing. Here, you can set “Allow access to unlicensed admins” to “Yes.”
It’s important to note that changes to this setting may take up to 48 hours to take effect, so plan accordingly when configuring admin access. This feature can be valuable for organizations that need to grant management privileges to users who do not have a license.
2. Directory services for Intune
Microsoft Intune offers a range of directory services options for consideration to integrate with your organization’s infrastructure:
- Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) serves as a directory service specifically designed for Microsoft Cloud Services. It is managed by Microsoft and supports authentication protocols like SAML, OAuth 2, and OpenID Connect.
- Windows Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is tailored for on-premises infrastructure and managed by the customer. It supports authentication protocols such as Kerberos and NTLM.
- Entra Domain Services is a directory service compatible with Windows Active Directory (Windows AD). This service is hosted and managed by Microsoft and supports authentication protocols like Kerberos and NTLM.
However, you’ll also want to consider directory service replication and how the directory services fit together as you plan your migration to Intune. Directory service replication plays a crucial role in ensuring the seamless integration and synchronization of user identities and devices across various directory services within the Microsoft ecosystem.
In Windows AD, organizations manage essential security principles such as users, groups, and domain-joined devices. To extend these capabilities to Microsoft Cloud Services (including Intune), you can use Entra Connect Sync to synchronize identities from Windows AD to Entra ID, ensuring consistent user management across on-premises and cloud environments.
Organizations can leverage Entra Domain Services to replicate users from Entra ID for specific use cases, but it’s important to note that this replication is one-way, with identities flowing from Entra ID to Entra Domain Services. This limitation is why Entra Domain Services does not support Entra Hybrid Join, a feature that combines on-premises and cloud identity capabilities.
3. The importance of auto-enrollment
As noted previously, auto-enrollment is an important feature, simplifying device onboarding and management by automating the enrollment process for devices joining an organization’s network. As organizations transition to Intune, it’s essential to consider the following aspects of auto-enrollment to ensure a smooth experience:
Automated device enrollment:
- Enables administrators to automatically enroll devices as soon as they join the organization’s network.
- Ensures that only authorized and authenticated devices are managed within the environment.
Directory services auto-enrollment:
- Entra ID — Intune supports auto-enrollment for Entra ID joined users and devices. Devices synchronized to Entra ID through Entra Connect Sync can be automatically enrolled.
- Windows AD DS — Devices can be configured for auto-enrollment into Intune.
- Entra Domain Services — Devices managed through Entra Domain Services do not synchronize to Entra ID for auto-enrollment.
Auto-enrollment mistakes to avoid:
- Verify device synchronization between Entra ID, Windows AD DS, and other directory services to ensure that enrolled devices are managed appropriately.
- Organizations should carefully configure Organizational Unit (OU) filters to ensure that auto-enrollment targets the intended devices and users within the directory services.
- For environments with multi-user devices running Windows 10 or 11, administrators must apply different settings to ensure proper Intune management based on user profiles.
- When dealing with virtualized client environments, such as virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), administrators should account for unique configurations, such as local admin login, domain join procedures, and remote access settings for Intune users.
4. Mobile Device Management vs Mobile Application Management
When preparing to move to Microsoft Intune, it’s important to understand the distinction between Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Mobile Application Management (MAM). MDM focuses on device-centric management, where the company owns and manages the entire device lifecycle:
- Device ownership: The company owns the device and is responsible for managing its features and settings.
- Enrollment: Devices are enrolled into Intune, allowing IT administrators to push device-specific applications and settings to these devices.
MAM, on the other hand, centers around user-centric management, particularly for personal devices (BYOD):
- User-centric approach: MAM focuses on protecting applications and data on personal devices used by employees.
- Application management: IT administrators can publish, configure, and manage specific applications on mobile devices without directly managing the entire device.
- Reporting: MAM allows for reporting on application inventory and usage, providing insights into how applications are being used across different devices.
MAM is particularly suitable for organizations looking to secure corporate data and applications on employees’ personal devices while respecting user privacy and device ownership.
5. Managing devices and users in Intune
When managing devices and users with Intune, several key features and capabilities come into play:
- Compliance policies: Intune allows the creation of compliance policies that define rules and settings to ensure devices meet specific security and compliance standards. These policies can cover a range of areas, such as encryption, device health, and app protection.
- Configuration profiles: Configuration profiles in Intune enable the centralized management of settings and features across devices. These profiles can be applied to different groups of devices or users, ensuring consistent configurations and security settings.
- Administrative templates: Intune supports administrative templates that allow administrators to configure device settings and apply policies using familiar Group Policy settings.
- Policy settings: Intune’s compliance policy settings include tenant-wide configurations, rules for devices without specific policies, and offline limits to ensure devices remain compliant even when disconnected from the network.
- Device compliance policies: Intune allows the creation of platform-specific compliance rules that define settings for device compliance. These policies can be user-based or device-based:
- User-based policies: Apply when MDM-enabled users log into a device.
- Device-based policies: Apply to devices without a primary user, ensuring compliance across the device regardless of the user.
When dealing with non-compliant devices in Microsoft Intune, administrators have several actions they can take to address the issue effectively:
- Mark the device as non-compliant: Intune allows administrators to flag devices that do not meet compliance standards as non-compliant. This designation helps track and manage devices that require attention.
- Email notification: Administrators can configure Intune to send email notifications when a device is marked as non-compliant. This alerting mechanism ensures that IT staff are promptly informed of compliance issues.
- Retire device: As a last resort, administrators can retire a non-compliant device. Device retirement removes corporate data and settings from the device, ensuring data security and compliance.
6. Configuring profiles for easier management
Configuring profiles is essential for managing device settings and configurations across different platforms like Android, iOS, and Windows. Similar to GPOs in Active Directory DS, Intune configuration profiles allow administrators to enforce specific settings based on device type. Top considerations for IT include:
- Device types and settings: Intune supports various device types, including Android, iOS, and Windows. Configuration profiles can be tailored to each device type, ensuring appropriate settings and controls.
- Differential configuration profiles: Different configuration profiles can apply to different device types. This flexibility enables administrators to customize settings based on the specific requirements of each platform.
- Administrative templates and baseline configuration: Intune leverages administrative templates and baseline configurations to streamline the deployment of settings across devices. These templates simplify the management of configurations and ensure consistency.
- Device and user assignments: Configuration profiles can be assigned to devices or users. Device-based assignments apply settings to a specific device, irrespective of the user. User-based assignments follow the user across different devices, ensuring a consistent experience.
7. Applications supported in Intune
Application management in Intune offers comprehensive support for various application types, ensuring flexibility and efficiency in deployment.
Supported application types:
Assignment types:
- Required: Applications installed automatically without user interaction.
- Available: Users can install applications from the Intune Company Portal.
- Uninstall: Remove existing applications deployed through Intune.
.intunewin file:
- Used to deploy Windows applications to devices managed by Intune
- This file is created using the Win32 Content Prep Tool, which converts Win32 applications into .intunewin format.
- But keep in mind that 30 GB is the maximum package size.
Nerdio—the final piece of the puzzle
Adopting Nerdio before transitioning to Intune offers several advantages to the migration process and beyond. It’s crucial to consider Nerdio’s comprehensive features that enhance Unified endpoint management (UEM) and streamline administrative tasks. Features that make Nerdio Manager an integral part of the move include:
- Unified application management (UAM): Allows centralized control and deployment of applications across diverse endpoints. This simplifies application delivery and ensures consistent user experiences.
- Granular RBAC roles for endpoint management: Granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) roles that enable fine-grained control over administrative privileges, enhancing security and governance.
- Policy and profile backup and versioning: Ensures that historical configurations are accessible, simplifying rollback procedures and supporting compliance requirements.
- Multi-tenant/cross-tenant policy management: Enables MSPs to efficiently manage policies across multiple clients, improving operational efficiency and scalability (Available only in Nerdio Manager for MSP).
Incorporating Nerdio into your cloud strategy establishes a robust foundation for deploying and managing Microsoft technologies, paving the way for a successful transition to Intune and beyond.
For more information about how Nerdio simplifies the deployment and management of Microsoft Intune while reducing costs for your organization, read our blog post From Cost to Value: The Nerdio Effect on Intune Management.


