NERDIO GUIDE

Customer story
Beyond a conference — NerdioCon 2026: Learning, networking & unforgettable moments.
Save your spot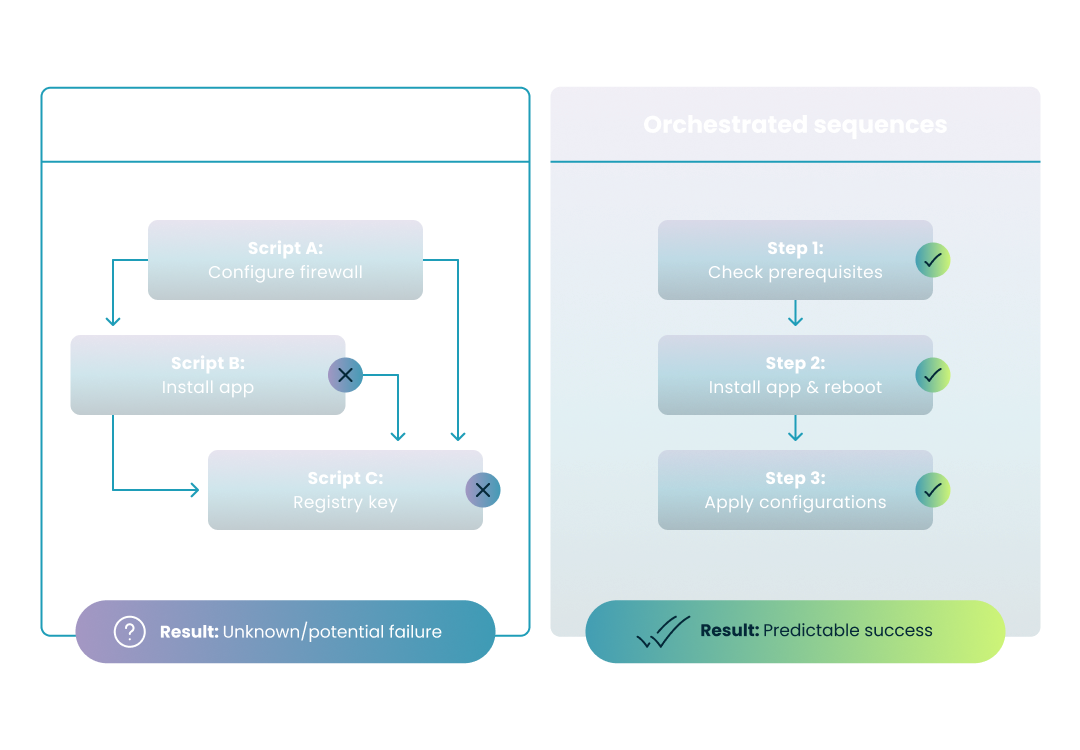
Intune script deployment is a critical method for automating device configuration and management across Windows, macOS, and Linux endpoints. By using scripts, you can execute complex administrative tasks that go beyond the standard configuration profiles available in Microsoft Intune.
Mastering these deployment practices ensures your environment remains secure, compliant, and standardized without requiring manual intervention on every device.
Microsoft Intune uses the Intune Management Extension (IME) to execute scripts on managed devices, filling the gap where native MDM policies might fall short. Understanding the distinction between a script and a Win32 app is essential for choosing the right tool for your specific administrative task.
While both can execute code, they serve different primary functions. You should use scripts for lightweight, "fire-and-forget" configurations, while Win32 apps are better suited for complex software installations.
PowerShell is the standard for Windows automation, allowing you to interface directly with the OS. It provides granular control over system settings that are not yet exposed in the Intune Settings Catalog. According to Microsoft, scripts allow for a highly customizable management experience, especially during the Initial Device Setup (Autopilot) phase. When a script is assigned, the Intune Management Extension serves as the client-side agent that checks for new assignments every 60 minutes to ensure the Windows device remains in sync with the latest configurations.
Preparing your scripts correctly is the difference between a seamless rollout and a wave of helpdesk tickets. You must consider the security context and the architecture of the host machine to ensure the script executes as intended.
The execution context determines what permissions the script has and which part of the registry it can access. Choosing the wrong context is a leading cause of script failure during deployment.
By default, Intune may attempt to run scripts in a 32-bit (x86) context, which can lead to "Registry Reflection" issues where changes are redirected to SysWOW64 instead of the intended system folders.
Best Practice: Always toggle the "Run script in 64-bit PowerShell host" to Yes unless you specifically need to interact with a 32-bit application. This ensures your script interacts with the modern 64-bit architecture found on most enterprise devices running Windows 10 or Windows 11 today.
Visibility is the most significant challenge in script management, as errors often occur silently when pushing updates to users. Without robust logging, you cannot verify compliance or troubleshoot why a deployment failed on a specific subset of devices.
Native Intune reporting is often delayed and only provides a basic "Success" or "Failure" status. To gain deeper insight, you should implement local logging within your PowerShell scripts. While standard tools offer a limited view of your deployment's health, enterprise-grade orchestration provides a "glass box" approach to management. This level of detail is a significant upgrade over native binary feedback, providing the deep visibility found in advanced reporting for Microsoft Intune to ensure administrators can verify compliance and performance across the entire fleet.
The following comparison highlights the "visibility gap" between binary reporting and granular, step-by-step logging.
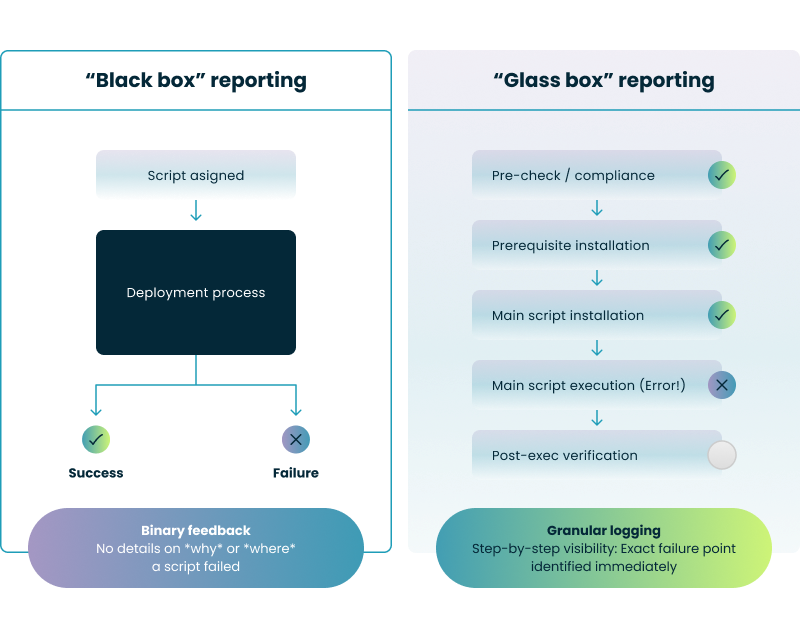
Let’s walk through the diagram above…
Native "Black Box" Reporting: Standard Intune deployment provides only a final status. If a script fails, IT admins are left "flying blind" without knowing exactly where it stopped.
Sequential "Glass Box" Visibility: Orchestration through Nerdio Scripted Sequences breaks the deployment into individual, trackable nodes.
Real-Time Failure Identification: By seeing exactly which step failed—such as a pre-check or a specific registry tweak—you can identify and remediate the root cause immediately rather than manually collecting device logs.
Contextualized Failure Data: Instead of a generic failure message, granular logging shows you exactly which environmental factor or prerequisite check caused a script to halt.
To move away from "binary feedback" and toward granular visibility, your script architecture must include these three elements:
Effective targeting ensures that your scripts reach the right devices without causing performance degradation or user interruptions. Proper scheduling and filtering are key components of a stable endpoint management strategy.
While both work, Microsoft recommends using Filters for script assignments whenever possible. Filters are evaluated at the time the device checks in, making them significantly faster and more accurate than dynamic groups, which can take hours to update.
Standard Intune scripts are designed to run once; they do not natively support recurring schedules without manual intervention.
| Standard Scripts | Intune Remediations | |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Runs once | Recurring schedule |
| Visibility | Low (Success/Fail) | High (Detection/Remediation state) |
| Best For | One-time configs | Compliance & Drift control |
A common frustration for IT admins transitioning from SCCM to Intune is the lack of native task sequences. In a standard Intune environment, scripts run asynchronously, meaning you cannot easily guarantee that "Script A" finishes before "Script B" begins.
When you push multiple updates or configurations simultaneously, they can conflict, leading to "race conditions." For example, if a script attempts to configure a piece of software before the installation script has finished, both actions may fail, leaving the device in a non-compliant state.
The visual below illustrates the 'race condition' risk of native, asynchronous scripting compared to the predictable success of orchestrated sequences.
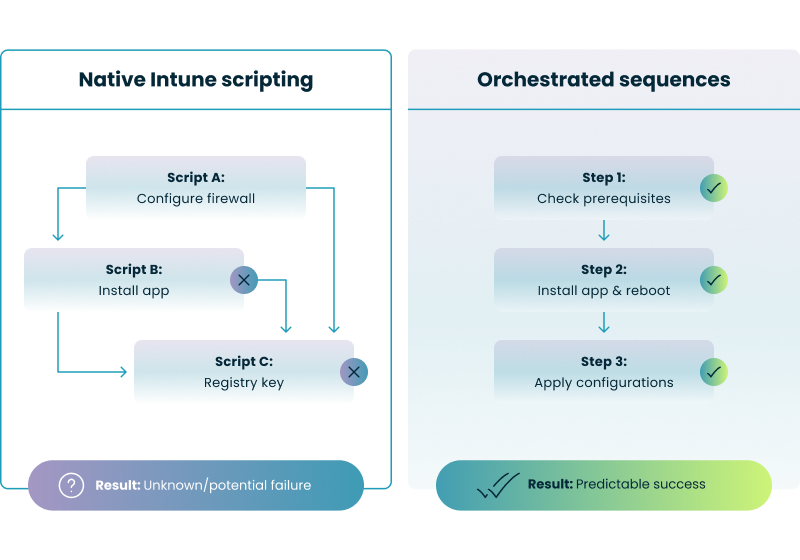
Guaranteed Order of Operations: Unlike native Intune, which triggers scripts simultaneously, orchestration ensures that "Step 2" never begins until "Step 1" confirms a successful exit code.
Eliminating Race Conditions: By enforcing a strict path, you prevent common conflicts where a configuration script tries to run before the application it’s targeting has finished installing.
Modular Management: Instead of building "monolithic scripts"—giant, hard-to-maintain files that handle everything at once—you can chain smaller, reusable scripts into a single logical flow.
Integrated Reboot Handling: Orchestration allows you to programmatically handle reboots between steps, ensuring the device is in the correct state for the next phase of the sequence without breaking the deployment.
Without third-party orchestration, admins often resort to "monolithic scripts"—combining many different tasks into one giant PowerShell file. This is difficult to maintain and troubleshoot. Another common workaround is using Win32 app "Dependencies," though this adds significant administrative overhead for simple configuration tasks.
Nerdio Manager for Enterprise provides the orchestration and visibility layer that is often missing in native Intune environments. By extending the core capabilities of the Microsoft Intune platform, Nerdio empowers administrators to handle complex automation scenarios that native tools alone cannot address. It allows IT professionals to move away from fragmented, one-off scripts toward reliable, automated workflows. For instance, Penn State University leveraged Nerdio's robust PowerShell integration to automate monotonous configuration tasks, successfully replacing manual efforts with highly reliable, repeatable enterprise workflows.
One of the primary causes of deployment errors is a lack of insight into the device state during an update. Nerdio’s Scripted Sequences allow you to chain together multiple scripts, applications, and even reboots into a single, logical flow.
Nerdio enhances the deployment process by integrating with your existing repositories, such as GitHub or Azure DevOps. This allows for:
By using Nerdio to manage these sequences, IT teams gain the "Task Sequence" power of SCCM with the cloud-native flexibility of Microsoft Intune, ensuring that every deployment is predictable, visible, and successful. This seamless orchestration is the cornerstone of a modern unified endpoint management strategy, harmonizing the administration of physical endpoints, Windows 365 management strategies, and Cloud PCs under one robust methodology.
Multi-tenancy presents increased security risks because a vulnerability in one tenant's environment can potentially affect others sharing the same underlying infrastructure. Additionally, "noisy neighbor" effects can occur when one tenant's high resource usage degrades performance for others, and individual tenants often have limited ability to customize their environment.
The Azure service lifecycle typically moves from a development phase to Private Preview, which is an invite-only stage for a small set of customers to provide early feedback. It then enters Public Preview for broader testing by any customer before reaching General Availability (GA), the stage where the service is fully supported with a formal Service Level Agreement (SLA).
Yes, a single Microsoft Entra ID tenant can be trusted by multiple Azure subscriptions at the same time. However, each individual Azure subscription can only have a trust relationship with exactly one Entra ID directory at any given time.
A session host should be joined to Microsoft Entra ID when you want to remove dependencies on traditional Active Directory Domain Controllers and simplify identity management. Enrollment in Microsoft Intune should follow Entra join when you need to enforce compliance policies, manage applications, and monitor device health at scale.
On average, businesses implementing process automation achieve an ROI of approximately 240%, with top-performing organizations reaching up to 390%. Most implementations see a full payback on their investment within six to nine months through significant gains in administrative efficiency and error reduction.



Carisa Stringer
Head of Product Marketing
Carisa Stringer is the Head of Product Marketing at Nerdio, where she leads the strategy and execution of go-to-market plans for the company’s enterprise and managed service provider solutions. She joined Nerdio in 2025, bringing 20+ years of experience in end user computing, desktops-as-a-service, and Microsoft technologies. Prior to her current role, Carisa held key product marketing positions at Citrix and Anthology, where she contributed to innovative go-to-market initiatives. Her career reflects a strong track record in driving growth and adoption in the enterprise technology sector. Carisa holds a Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology.